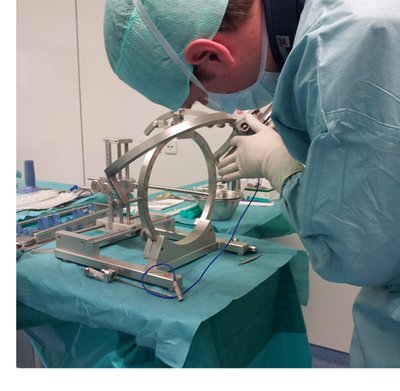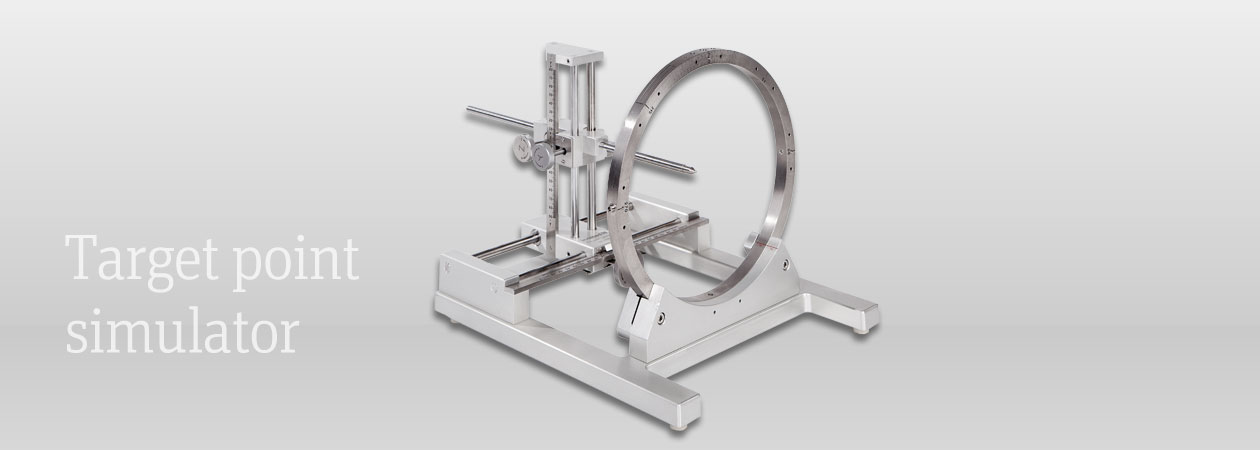
inomed's stereotactic target point simulator, also known as the Phantom, is a unique tool and is exclusively available at inomed. Professors Riechert and Mundinger, who are recognized worldwide as pioneers in neurosurgery, created the Phantom in parallel with the development of the RM >> stereotactic system.
The target point simulator has established itself internationally and is considered by leading neurosurgeons to be an indispensable and recommendable tool for planning and performing complex operations on the brain. The phantom's use becomes particularly important in the highly complex techniques of neuromodulation (DBS).
The target point simulator (phantom) is primarily used to convert the coordinates of the planning software and to mechanically set the target point in real space before operation. A steel target point rod is moved in the X, Y, and Z axes (coordinates from the planning software) using three movable thumbscrews. This rod's tip forms the patient specific target point, accordingly to the planning software. A base ring is attached to the target point simulator, onto which the stereotactic arc can be placed. The phantom thus simulates the individual target points for each patient and hemisphere.